4.2 The Vertex-Distance-Path Matrix
The vertex-distance-path matrix, denoted by vDp,
was introduced by Diudea [218,219]. Its entries
are based on the elements of the vertex-distance matrix:
[ vDp] ij= 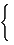 |
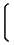 |
[vD]ij + 1 |
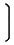 if i ≠ j if i ≠ j |
2 |
|
| 0 otherwise (46) |
It should be noted that the elements [vDp]ij count all internal paths included in the shortest paths between vertices i and j in a graph. An algorithm which finds all paths on a graph (molecular skeleton) has been devised by Randić et al. [220].
As examples of the vertex-distance-path matrices of (molecular) graphs, we give vDp matrices of T2 and G1 (see structure A in Figure 2):
vDp(T2)= |
|
0 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
10 |
15 |
6 |
3 |
 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
10 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
6 |
10 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
6 |
10 |
15 |
10 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
10 |
15 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
10 |
0 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
10 |
15 |
6 |
0 |
vDp(G1)= |
|
0 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
10 |
6 |
10 |
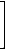 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
10 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
10 |
6 |
3 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
The vertex-distance-path matrix allows the direct computation of the hyper-Wiener index [219,377].
<< . . . >>
