5.16 The Quotient Matrices
Quotient matrices have been introduced by Randić [330] and applied to structure-property modeling by Nikolić et al. [261] and Plavšić et al. [331]. The quotient matrices, denoted by Ma/Mb, are obtained by dividing the off-diagonal elements of matrices Ma and Mb:
vD/DM(G1)= |
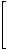 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0.6 |
1 |
0.6 |
0.67 |
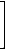 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0.33 |
1 |
0.33 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
0.5 |
0.33 |
0 |
0.33 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0.33 |
0 |
0.33 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
0.5 |
0.33 |
1 |
0.33 |
0 |
1 |
0.67 |
0.6 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
0 |
The molecular index based on the vertex-distance/detour matrix is called the Wiener-sum index [330] .
DM/vD(G1)= |
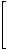 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1.67 |
1 |
1.67 |
1.5 |
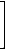 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1.67 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
1.67 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
2 |
1.67 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
1 |
1.5 |
1.67 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
The molecular index based on the detour/vertex-distance matrix is called the detour-sum index [331] .
vD/Ω(G1)= |
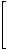 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1.09 |
1.33 |
1.09 |
1.07 |
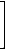 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.14 |
1.5 |
1.14 |
1.09 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1.33 |
2 |
1.33 |
1.14 |
1.09 |
1.14 |
1.33 |
0 |
1.33 |
2 |
1.5 |
1.33 |
1.5 |
2 |
1.33 |
0 |
1.33 |
1.14 |
1.09 |
1.14 |
1.33 |
2 |
1.33 |
0 |
1 |
1.07 |
1.09 |
1.14 |
1.5 |
1.14 |
1 |
0 |
The molecular index based on the vertex-distance/resistance-distance matrix is a variant of the Wiener-sum index [277] .
Ω/vD(G1)= |
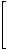 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0.92 |
0.75 |
0.92 |
0.93 |
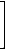 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0.88 |
0.67 |
0.88 |
0.92 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0.75 |
0.5 |
0.75 |
0.88 |
0.92 |
0.88 |
0.75 |
0 |
0.75 |
0.5 |
0.67 |
0.75 |
0.67 |
0.5 |
0.75 |
0 |
0.75 |
0.88 |
0.92 |
0.88 |
0.75 |
0.5 |
0.75 |
0 |
1 |
0.93 |
0.92 |
0.88 |
0.67 |
0.88 |
1 |
0 |
The molecular index based on the resistance-distance/vertex-distance matrix is called the Kirchhoff-sum index [277]. Matrices vD/W and W/vD have been used to study the graph cyclicity [332].
vD/vcD(G1)= |
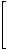 |
0 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
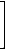 |
0.2 |
0 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.2 |
0 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.2 |
0 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.2 |
0 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
0.2 |
0 |
0.2 |
2 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.2 |
0 |
vcD/vD(G1)= |
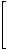 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
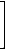 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
5 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
Two variants of the Balaban index [213] have been derived from the vD/vcD and vcD/vDmatrices [261] .
<< . . . >>
